In the last series, Eduriefy covered the important aspects of the Stone Age: A Journey to Transition. int his post we will focus on the Harappan civilization This series will take you down the lanes of Harappa and MohenjoDaro which has many things to say about the past.
Some of the Important Points about the Harappan Civilization
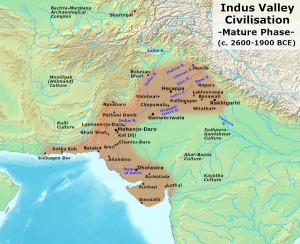
Around 3300 BC, the Indus Valley Civilization emerged. Between 2600 BC and 1900 BC, it was in full bloom (Mature Indus Valley Civilization). Around 1900 BC, it started to deteriorate, and around 1400 BC, it vanished.
- In honor of the first city to be discovered and excavated, Harappa is also known as the Harappan Civilization (Punjab, Pakistan).
- The earliest indications of cotton agriculture can be found in the Pre-Harappan civilization discovered in Mehrgarh, Pakistan.
- This civilization was geographically spread across Punjab, Sindh, Balochistan, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Western Uttar Pradesh. In addition, it stretched from Mandu (Jammu) in the north to Daimabad (Ahmednagar, Maharashtra) in the south, from Sutkagendor (in Balochistan) in the west to Alamgirpur (Western UP) in the east. Additionally, some Indus Valley sites have been discovered in Afghanistan and Turkmenistan.
Discovery of Harappa
Sir John Marshall made the initial excavations of the Harrapan civilization in 1921. South Asia was home to a bronze-age civilization. In the basins of the Indus River, the Indus Valley civilization developed. This civilization covered a large territory that included the Indus Plain, Northern Rajasthan, and the Kathiawar region of Western India.
Important Cities of the Harappan Civilization and its Importance
1)Mohenjo-Daro, located in Sind, Pakistan:-It was one of the biggest cities in the Indus Valley, and it was located on the right bank. People used to take a spiritual bath there where the large bath was located. The greatest structure was the Granary, a massive rectangular edifice with several pillars used as an assembly hall.
2. Kalibangan (Rajasthan)
In the Rajasthani area of Ganganagar, where the name Kalibangan means “black bangles,” this location is found on the southern bank of the Ghaggar rivers. Pre-Harappan and Harappan cultural periods were present in the city. The parallelogram citadel was found during the Pre-Harappan phase.
- Gujarat’s Lothal and Dholavira
In Gujarat, near the Gulf of Khambhat, Lothal is situated next to a Sabarmati tributary, while Dholavira is in the Kutch district. Evidence on lothal has also been found.
4. Harappa:
It is the earliest Indus site to have been excavated, beginning in 1921, and is situated on the left bank of the Indus River.
Life in the city of Harappa:
The people enjoyed dancing, singing, fishing, gambling, and other activities. The society was found to be matriarchal, with merchants as its dominant group. Both men and women were fond of ornaments (such as necklaces, finger rings, bangles, anklets, and bracelets).
- Street, Houses, and Drains:
Houses were two stories tall, the rooms were arranged around a courtyard, water overflowed from the houses’ drains onto the street, an underground drainage system had been established, the drains were lined with bricks to demonstrate their concern for sanitation, and grid systems were widespread.
Decline of Harappan Civilization
- The reasons for this civilization’s demise are not well understood. Archaeologists now think that the civilization fell gradually rather than abruptly. As people moved east, cities were left in ruins. Writing and commerce fell.
- The Aryan invasion, according to Mortimer Wheeler, may have contributed to the Indus Valley’s downfall. This idea has since been refuted.
- Robert Raikes contends that the fall was brought on by tectonic shifts and floods.
- Rivers drying up, deforestation, and loss of vegetation are a few more reasons given. It’s probable that some cities, but not all, were completely destroyed by floods. It is widely acknowledged that several events may have contributed to the Indus Valley civilization’s demise.
- There were only roughly 1400 new cities.
FAQs
Q: When did the Harappan Civilization reach its peak? A: The civilization reached its mature phase between 2600-1900 BCE.
Q: What makes the Harappan Civilization unique? A: It was one of the world’s first urban civilizations with sophisticated city planning, drainage systems, and standardized weights and measures.
Q: Why did the civilization decline? A: Multiple factors contributed, including environmental changes, social transformation, and possible climate change. Modern research suggests a gradual decline rather than a sudden collapse.
Recent Discoveries and Research
- Latest archaeological findings continue to reveal new aspects of this ancient civilization
- Modern technology helps reconstruct city layouts
- DNA studies providing insights into population movements
Key Takeaways
- The first urban civilization of South Asia
- Advanced architectural and engineering capabilities
- Sophisticated social and economic systems
- Gradual decline rather than sudden collapse
- Continuing influence on the Indian subcontinent’s cultural development
These were the details about the Indus Valley or the Harappan Valley Civilization. Stay tuned with Edureify to know about “The Rig Vedic Phase”.
Master Your Coding Skills with BootSelf AI
If you're looking to enhance your coding abilities and upskill in artificial intelligence, look no further than the BootSelf AI app. This innovative platform provides AI-based coding lessons that are tailored to your individual learning pace.
Available on both iOS and Android, you can download the BootSelf AI app and start mastering coding skills today:





